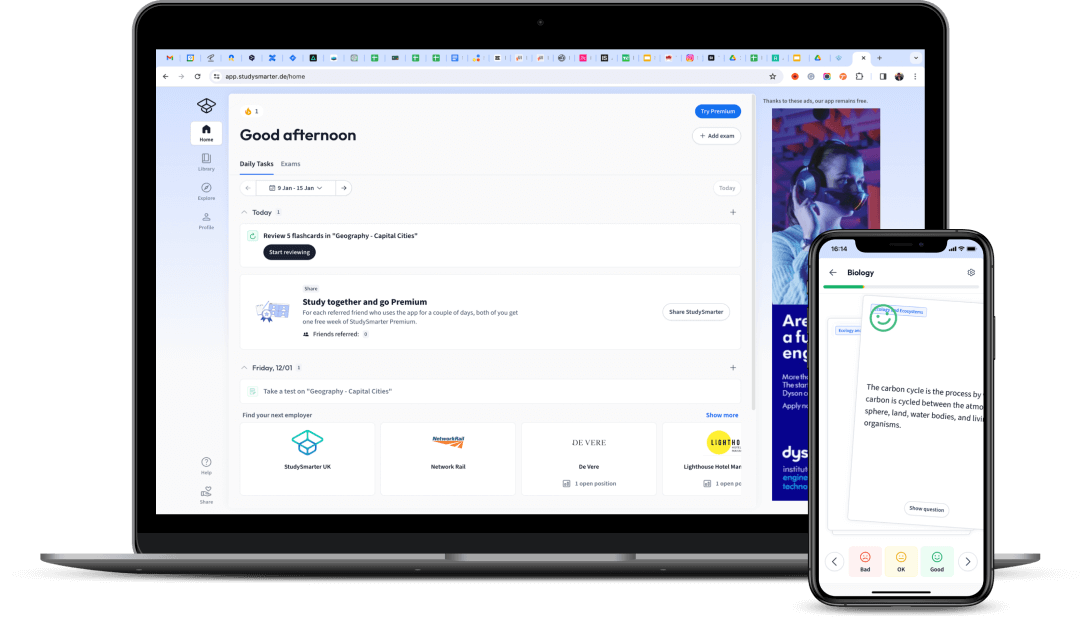
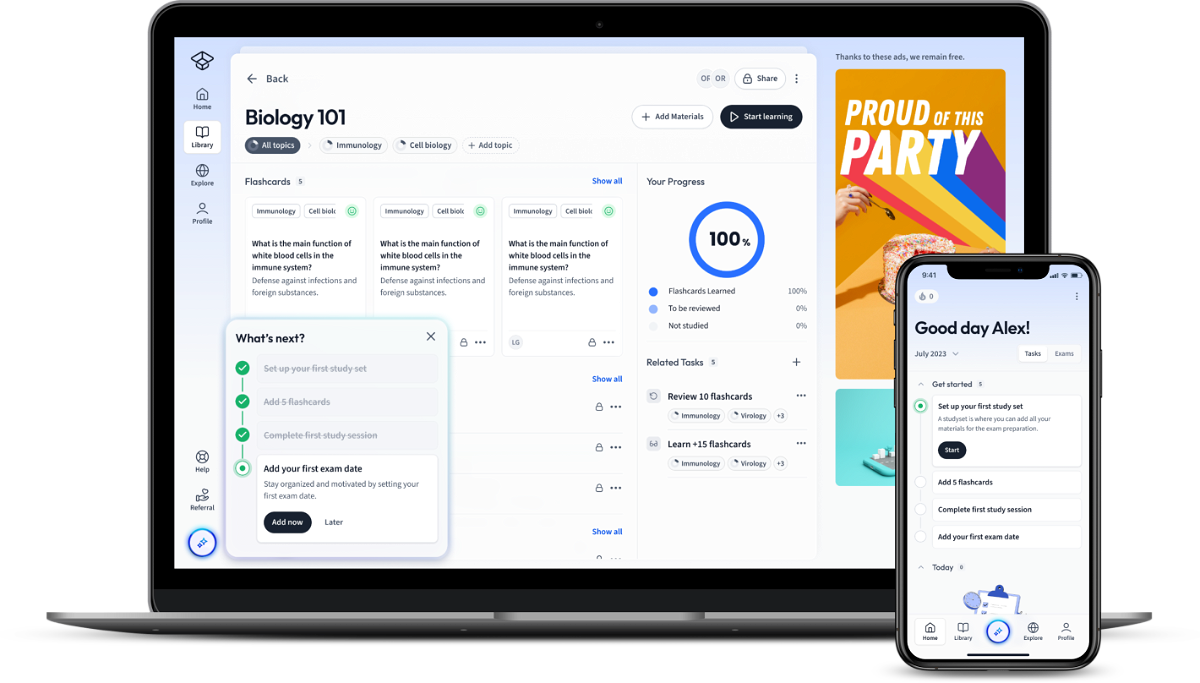
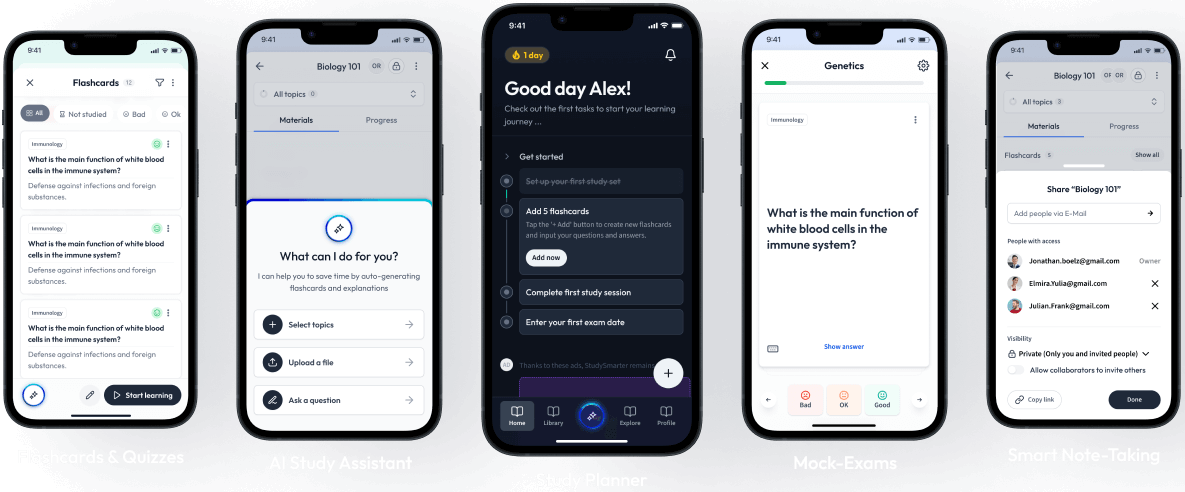
Words, words, words, and even more words! But what's the meaning behind them? Words can be used to describe what's invisible to the eye, to evoke feelings, create new worlds, and express ideas. English Literature is the subject of words and texts.
StudySmarter's English Literature Revision and Notes will show you how the stories we tell shape our culture and society. Reading literature expands our minds and our knowledge of the world and develops our imagination and emotional intelligence.
The poem 'Paradise Lost' (1667) by John Milton contains 8,000 different words. Can you imagine not only knowing that many words but also managing to include them in the same text?
English literature topics and learning objectives
From novels to literary devices, Study Smarter covers a variety of topics and learning objectives in English literature. Our high-quality content is accessible, making it easier for you to prepare for your English literature courses and exams.
English Literature: Novelists
Novelists are writers of novels. A novel is a book of long narrative fiction which usually centres around a main plot and follows characters as they develop. There are a variety of novel genres, such as gothic, dystopian, fantasy, and romance, that are enjoyed by readers with different preferences. Novels in English literature have continued to evolve through the ages, from the Renaissance to the present day.
Some of the novelists and works we cover include:
English Literature: Poets
Poets are authors of poems. A poem is a literary text that uses meter or rhythm – like a song without music. There are different types of poems, ranging from lyrical to narrative. Poets have existed since prehistoric times when their poems would travel from mouth to mouth. Poetry in English literature has gone through many transformations throughout the different historical periods.
StudySmarter will help you learn about poets and poems, such as:
English Literature: Dramatists
Dramatists (or playwrights) are authors who write dramas. A drama, also referred to as a play, is a work of fiction that is written to be performed in front of an audience, usually in a theatre. Dramas fall into different genres, the main ones being tragedy and comedy. Western drama originated in Classical Greece and continues to flourish. Dramatists in English literature have greatly contributed to the advancement of playwriting.
Some of the dramatists and plays we cover include:
English Literature: Non-fiction Authors
Non-fiction authors are writers who create texts that convey fact rather than fiction. Non-fiction refers to any text that is based on real events and delivers information based on factual truth. Non-fiction is often more objective than fiction. There are different types of non-fiction, including biography, history, and travel.
StudySmarter will help you discover non-fiction authors and works, including:
English Literature: Literary Devices
We use literary devices to determine the form and genre of literary works and to make sense of the different techniques that authors use. Which literary devices are used depend on the type of literature. Different literary devices are used in fiction, poetry, drama, or non-fiction texts.
Fictional devices include:
Poetic devices include:
Dramatic devices include:
English Literature: Literary Movements
Literary movements show us what literary genres and types of works were prevalent in specific time periods. We cover all the movements in English literature:
Old English (450–1066): poetry.
Middle English (1066–1500): poetry.
The Renaissance (1500–1660): poetry, drama.
The Elizabethan Age (1558–1603): drama.
The Jacobean Age (1603–25): prose (treatise), drama.
The Restoration Period (1660–1700): prose, drama.
The Romantic Period (1785–1832): poetry, prose, drama.
The Victorian Period (1832–1901): prose (novels), poetry, drama.
Modernism (1914–45): prose (novels), poetry.
Postmodernism (1945–present): prose, poetry, drama.
English Literature: Literary Elements
A literary text is made of different literary elements. StudySmarter can help you explore the diverse components that are used to construct a body of text, including:
English Literature: Literary Criticism and Theory
When reading a text, we think about its meaning. The ability to analyse literary works from different points of view is a vital skill. This is why literary criticism, or the practice of interpreting literature, is important. Literary theory is the study of literary works through different approaches.
Some of the literary theory approaches that we cover include:
How can StudySmarter support me in studying English literature?
StudySmarter makes learning and revision for your English literature courses and exams easy! We offer a range of resources that are not only efficient but also fun to use.
English Literature Revision Guide
Our intelligent guide is here to introduce everything you need to revise your English Literature courses and exams successfully. Here is what you can discover with StudySmarter:
English Literature Explanations
English Literature explanations provide overviews, analyses, and definitions of the wide range of topics in English Literature. Our explanations also introduce in-depth information and fun facts that you may not have known about before. For example, how much do you know about the Shakespeare Authorship Question? Did you know there's a theory that Shakespeare's works were written by a group of people and not by a single person? Learn more about Shakespeare and other authors with our English Literature explanations. You also have the handy option to upload your own notes.
English Literature Flashcards
English literature flashcards are the perfect revision tool! You can use the flashcards to answer questions that are directly related to the information covered in the English literature explanations. And don't worry if you can't think of the right answer – the flashcards will show it to you. You can also create your own personalised flashcards depending on what you need to revise for most.
English Literature Study Groups
Tired of revising on your own? StudySmarter gives you the opportunity to form study groups with other students. You have the chance to quiz your fellow peers on English literature topics, and you can get each other ready for your exams.
Rewards for learning English Literature
StudySmarter provides you with a fun and interactive system that will help you reach your full potential. You can set different weekly goals and gain trophies every time you complete a specific task – if you answer five English literature questions in a row, you'll become a Grandmaster! StudySmarter inspires you to keep learning by rewarding you for your achievements.
Explanations
Exams
Magazine